Learning Rust the Hands-On Way
Performant Software Systems with Rust — Lecture 2
Baochun Li, Professor
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
University of Toronto
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
University of Toronto
Rust is one of the most exciting languages in the recent years
Yet, it is known to be a complex language with a steep learning curve
But I’ve got some good news for you.
It can be simple if you learn it the hands-on way.
Advanced, yet friendly, compiler
Unhelpful, cryptic errors abound
JSONDecodingError On Line 1
NullPointerException
IndexError In File <in>
Read the errors carefully
and the compiler will teach you itself
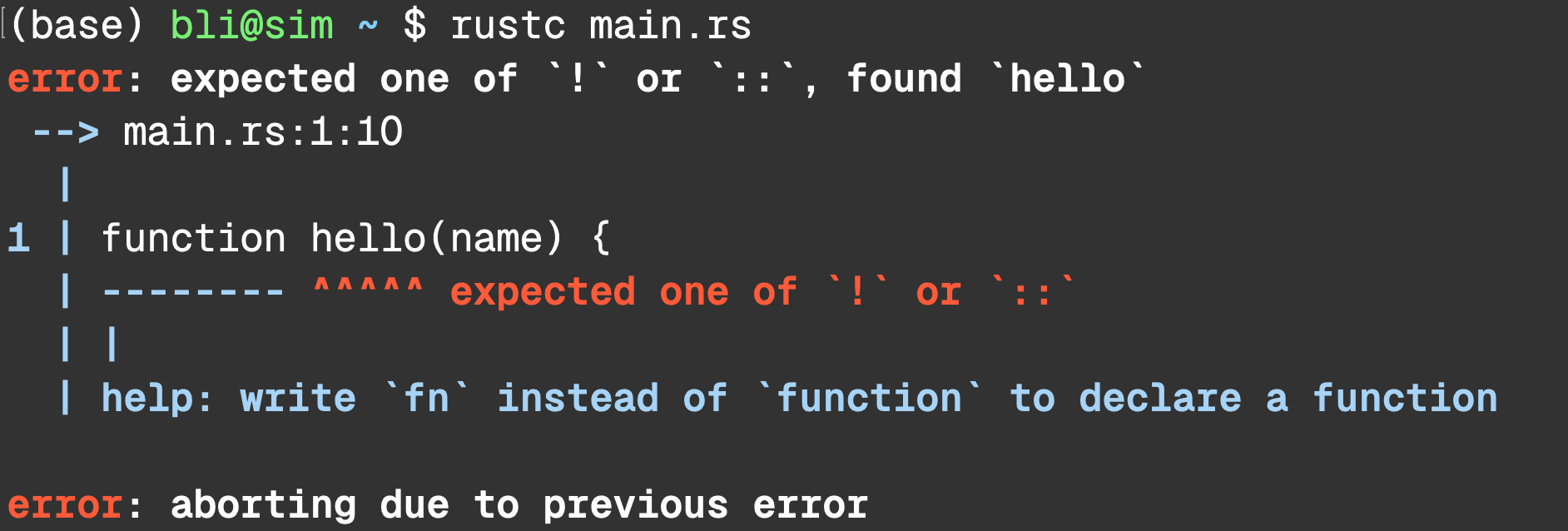
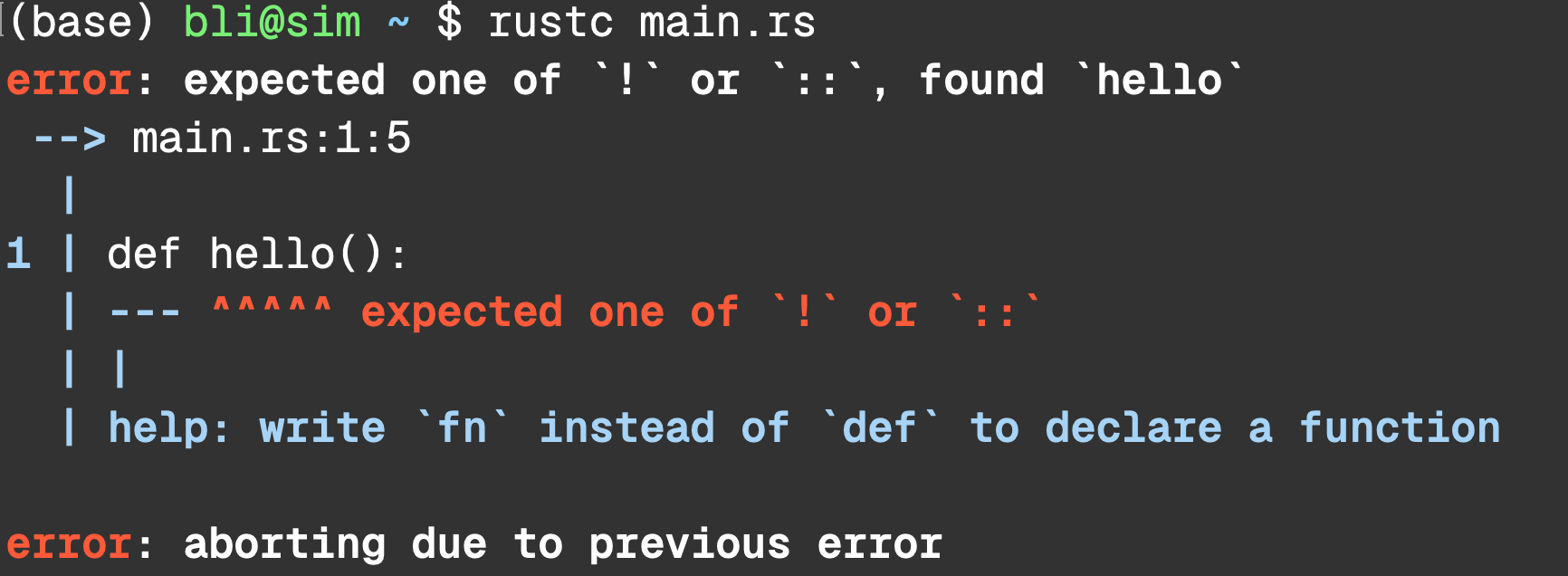
Let’s Write Some Rust Javascript
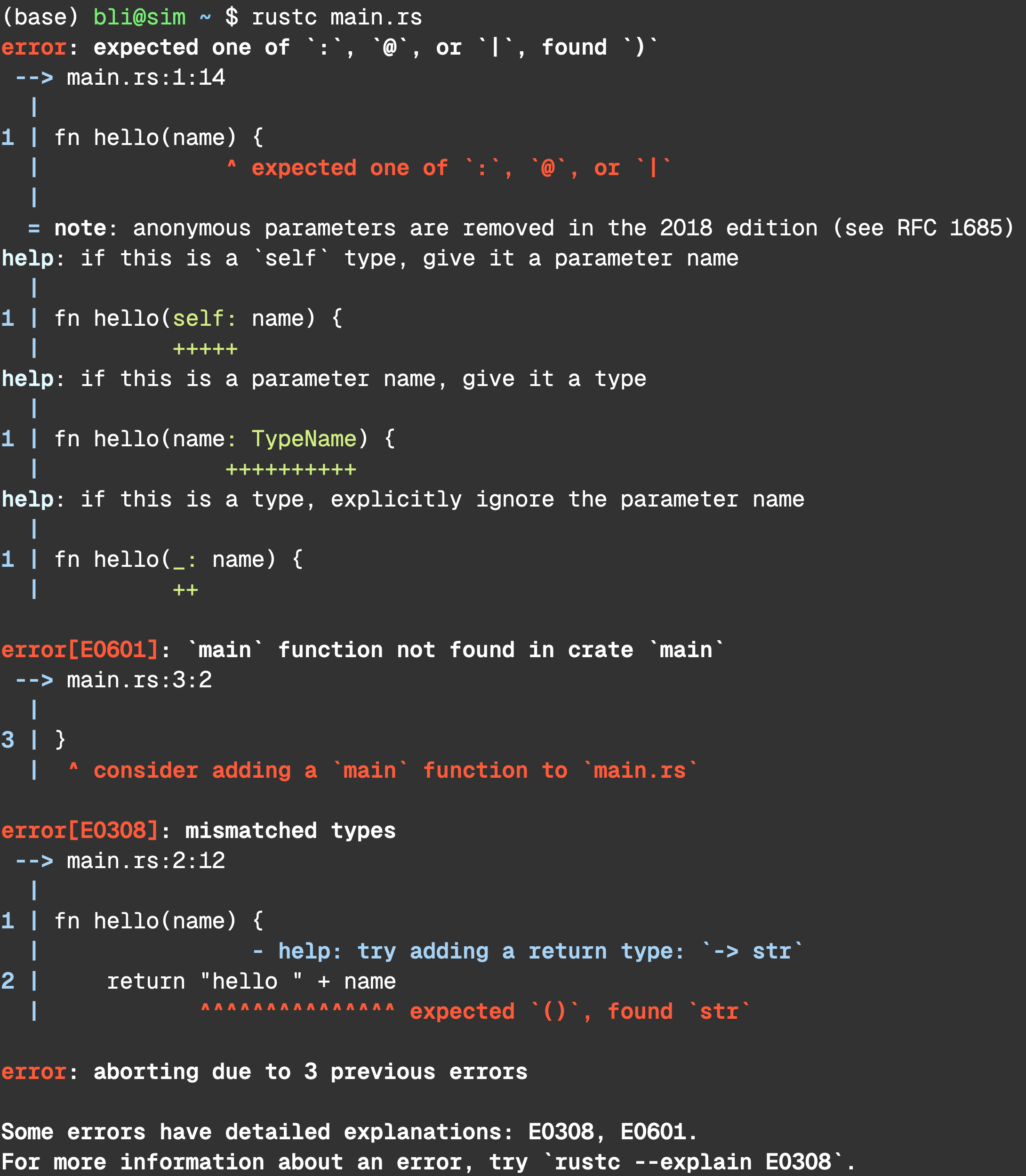
error: expected one of `:`, `@`, or `|`, found `)`
--> main.rs:1:14
1 | fn hello(name) {
| ^ expected one of `:`, `@`, or `|`
|
help: if this is a `self` type, give it a parameter name
|
1 | fn hello(self: name) {
| +++++
help: if this is a parameter name, give it a type
|
1 | fn hello(name: TypeName) {
| ++++++++++
help: if this is a type, explicitly ignore the parameter
|
1 | fn hello(_: name) {
| ++error[E0369]: cannot add `String` to `&str`
--> main.rs:2:21
|
2 | return "hello " + name
| -------- ^ ---- String
| | |
| | `+` cannot be used to concatenate
| a `&str` with a `String`
| &str
|
help: create an owned `String` on the left
and add a borrow on the right
|
2 | return "hello ".to_owned() + &name
| +++++++++++ +error[E0369]: cannot add `String` to `&str`
--> main.rs:2:21
|
2 | return "hello " + name
| -------- ^ ---- String
| | |
| | `+` cannot be used to concatenate
| a `&str` with a `String`
| &str
|
help: create an owned `String` on the left
and add a borrow on the right
|
2 | return "hello ".to_owned() + &name
| +++++++++++ +error[E0369]: cannot add `String` to `&str`
--> main.rs:2:21
|
2 | return "hello " + name
| -------- ^ ---- String
| | |
| | `+` cannot be used to concatenate
| a `&str` with a `String`
| &str
|
help: create an owned `String` on the left
and add a borrow on the right
|
2 | return "hello ".to_owned() + &name
| +++++++++++ +error[E0369]: cannot add `String` to `&str`
--> main.rs:2:21
|
2 | return "hello " + name
| -------- ^ ---- String
| | |
| | `+` cannot be used to concatenate
| a `&str` with a `String`
| &str
|
help: create an owned `String` on the left
and add a borrow on the right
|
2 | return "hello ".to_owned() + &name
| +++++++++++ +error[E0369]: cannot add `String` to `&str`
--> main.rs:2:21
|
2 | return "hello " + name
| -------- ^ ---- String
| | |
| | `+` cannot be used to concatenate
| a `&str` with a `String`
| &str
|
help: create an owned `String` on the left
and add a borrow on the right
|
2 | return "hello ".to_owned() + &name
| +++++++++++ +error[E0369]: cannot add `String` to `&str`
--> main.rs:2:21
|
2 | return "hello " + name
| -------- ^ ---- String
| | |
| | `+` cannot be used to concatenate
| a `&str` with a `String`
| &str
|
help: create an owned `String` on the left
and add a borrow on the right
|
2 | return "hello ".to_owned() + &name
| +++++++++++ +Let’s try running rustc --explain E0308
Expected Type Did Not Match the Received Type
The Compiler Teaches You
https://rustup.rs
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
Beautiful one-liner install
- except if you are running Windows
Updating Rust
rustup update
Local Offline Docs
rustup doc
Or directly open the Rust Book
rustup doc --book
Hello World
Compiling Your Code
rustc main.rs
Creating a Project with Cargo
Three items have been created for you
Cargo.tomlsrc/main.rs- local git repo
Cargo.toml
Building Your Project
Running Your Project
Checking Your Project
Cargo: Swiss Army Knife
cargo doc # local package documentation
cargo bench # built-in benchmarking
cargo test # built-in parallel testing
cargo add aws-sdk # easily add dependencies
cargo install # install exes into .cargo/bin
cargo clippy # run the code linter
cargo publish # publish packages to crates.ioModern Tooling
- cargo - packaging, building
- cargo fmt - standard formatting
- cargo test - doc and unit tests
- cargo bench - benchmarking
- cargo clippy - code linting
- rustup - rust version switching
Additional Resources
Everything related to Rust on fasterthanli.me
Rust By Example https://doc.rust-lang.org/rust-by-example/
- follows the same chapter ordering to the Rust Book
Rust
Your code can be perfect
Our First Rust Project
The Guessing Game
Demo
Generating a Secret Number
Cargo.toml
Updating Crates
Generating a Random Number
Consulting local docs
cargo doc --open
Comparing the Guess to the Secret Number
Demo
Resolving the Compile-Time Error
Adding a Loop
Quitting after a Correct Guess
Handling Invalid Input
You have just built your first Rust project!
Required Additional Reading
The Rust Programming Language, Chapter 1-2