Basic Programming Concepts
Performant Software Systems with Rust — Lecture 3
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
University of Toronto
Teaching style in this course — examples and demos
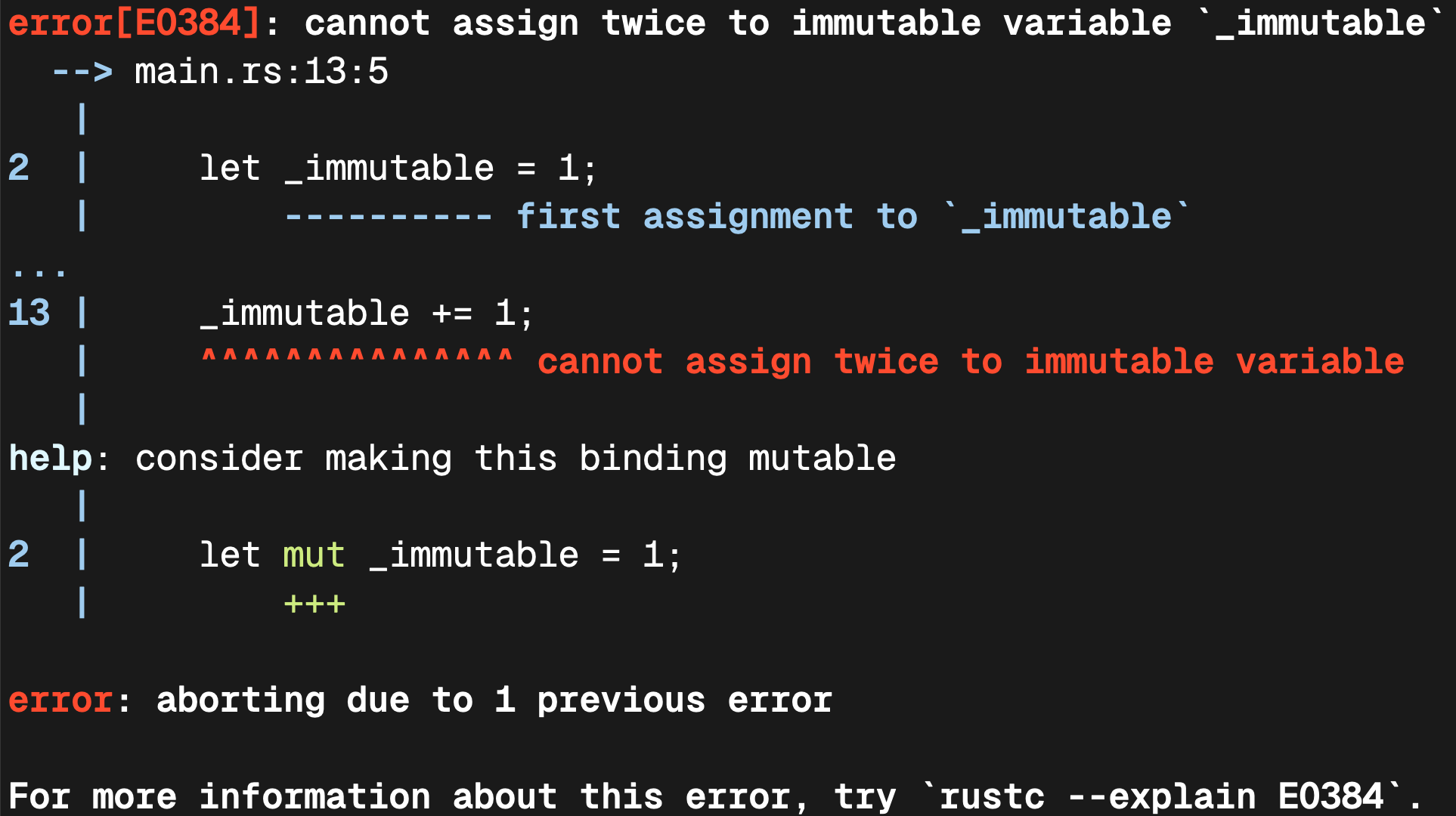
Mutable and immutable variables
Variables are immutable by default — you are allowed to bind a value to an immutable variable only once
Learn more: Variables and Mutability
Learn more: Variables and Mutability
Constants
Naming convention: all upper case with underscores
const: a constant value that can be completely computed at compile timeany code that refers to them is replaced with the constant’s computed value at compile time
Just a convenient name for a particular value
static: global variable (may only be modified withunsafe)Both constants and globals need explicit type annotation
Learn more: Constants
Contants
Learn more: Constants
Demo: Constants and Globals
Learn more: Constants
Scope and Shadowing
- Scope
- Variable bindings are constrained to live in a block
- A block is a collection of statements enclosed by braces
{ }
- Shadowing
- Okay to declare a new variable with the same name as a previous variable
Learn more: Scope and Shadowing
Shadowing in the Guessing Game
Learn more: Scope and Shadowing
Data Types
Rust is a statically typed language — the compiler must know the types of all variables at compile-time
Why is Rust designed as a statically typed language?
Before we talk about the benefits of static types, let’s take a look at why Javascript and Python use dynamic types
Rust vs. Javascript
Rust
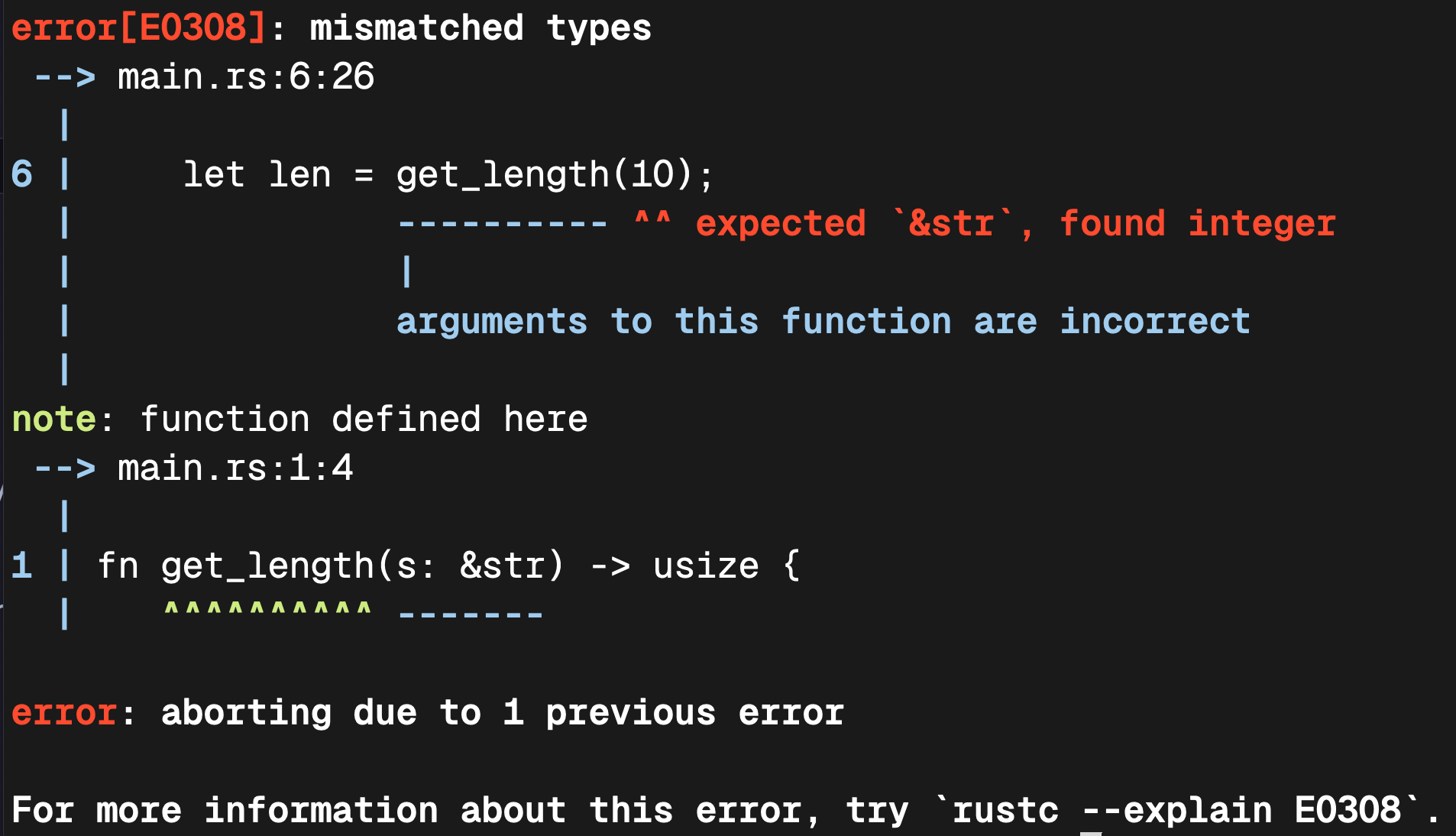
But what if we wish to add two floating-point numbers?
But what are the benefits of static types, then?
Rust vs. Python — Rust
Rust vs. Python — Python
Run-time errors \(\rightarrow\) compile-time errors
But can’t run-time errors be easily caught and fixed in Python?
Rust vs. Javascript — Javascript
Logical errors \(\rightarrow\) compile-time errors
Static types and Rust’s strict compiler make it much easier to catch all kinds of errors!
Scalar Data Types
Integer Types
| Length | Signed | Unsigned |
|---|---|---|
| 32-bit | i32 |
u32 |
| arch-dep | isize |
usize |
Learn more: Data Types
Floating-Point Types
| Length | Type |
|---|---|
| 32-bit | f32 |
| 64-bit | f64 |
Learn more: Data Types
Numeric Operations
Learn more: All Operators in Rust
The Boolean Type
Learn more: Data Types
The Character Type
Learn more: Data Types
Compound Data Types
The Tuple Type
Groups together some values with a variety of types
Once declared, cannot grow or shrink in size
Useful when a function needs to return multiple values
Learn more: Data Types
Using Pattern Matching to Destructure Tuples
Learn more: Data Types
Accessing Elements of a Tuple
Learn more: Data Types
The Unit Type: The Tuple Without Any Values
- The value and its type are both
() - Empty value and empty type
- Returned by expressions and functions if they do not return any other value
Learn more: Data Types
The Array Type
- Arrays have a fixed length
- Space for data in arrays are allocated on the stack
- Use vectors if you wish to grow or shrink in size
Learn more: Data Types
What if you try to access an element outside the bounds of an array?
Rust will panic, but only at run-time, because the compiler can’t possibly know the value used to index the array!
Functions
- We have seen them before already
- No restrictions on the order of function definitions
- The return type is declared after
->(the unit type()is the default) - The last expression in the function is the return value
Learn more: Functions
Functions
Learn more: Functions
Control Flow — if Expressions
- Same as C but no need for parentheses
- Just like any expression, it evaluates to a value
Learn more: Control Flow
Control Flow — if Expressions
Learn more: Control Flow
let big_n =
if n < 10 && n > -10 {
println!(", and is a small number, increase ten-fold");
// This expression returns an `i32`
10 * n
} else {
println!(", and is a big number, halve the number");
// This expression must return an `i32` as well
n / 2 // Try suppressing this expression with a semicolon
}; // Don't forget to put a semicolon here
println!("{} -> {}", n, big_n);
}Learn more: Control Flow
Repetition with Loops — loop
A loop loop can return a value with the break keyword
Learn more: Loops
Repetition with Loops — while
A while loop is just like C, minus the parentheses
Learn more: Loops
Repetition with Loops — for
- Concise — typically used to iterate through a collection
- Safer than iterating using an index — most often used
Learn more: Loops
Required Additional Reading
The Rust Programming Language, Chapter 3